low end tidal co2 during cpr
A sustained drop or low. Two very practical uses of waveform capnography in CPR are.

End Tidal Co2 Emergency Medicine Icu Nursing Paramedic School
Low ETCO2 below 10 mm HG may be caused by either poor compression technique or from low perfusion and metabolism after a long downtime or shock despite good compressions.

. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO2 production and clearance ventilation. Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram. PaCO2 PetCO2 End tidal measurement from expired or exhaled air PaCO2 Arterial blood gas sample End tidal normally 2-5 mmHg lower than arterial Comparing Arterial and End-tidal CO2 Review of Airway Confirmation Visualization Auscultation.
Why is ETCO2 low during CPR. 1 evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions and 2 High quality chest compressions are achieved when the ETCO2 value is at least 10-20 mmHg. Low EtCO 2 with other signs of shock indicates poor systemic perfusion which can be caused by hypovolemia sepsis or dysrhythmias.
Chest compression provider tiring end-tidal CO2 value diminishes over time. What does end-tidal CO2 tell you. Thus ETco 2 monitoring is a noninvasive way to measure coronary artery blood flow and return of spontaneous circulation during CPR.
In critical care End Tidal CO 2 monitoring is used to assess adequacy of circulation to the lungs which provides clues about circulation to the rest of the body. Uses during cardiac arrest. Measuring end-tidal CO2 in cardiac arrest patients is helpful for confirming tracheal tube placement assessing the effectiveness of chest compressions predicting likelihood of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC in that a persistently low ETCO2 tends to predict death whereas a high or rising ETCO2 is associated with a higher chance of ROSC.
Negative Epigastric sounds Equal lung sounds Esophageal detector. End-tidal carbon dioxide. This will cause a decrease in the ETCO2 end-tidal CO2 and this will be observable on the waveform as well as with the numerical measurement.
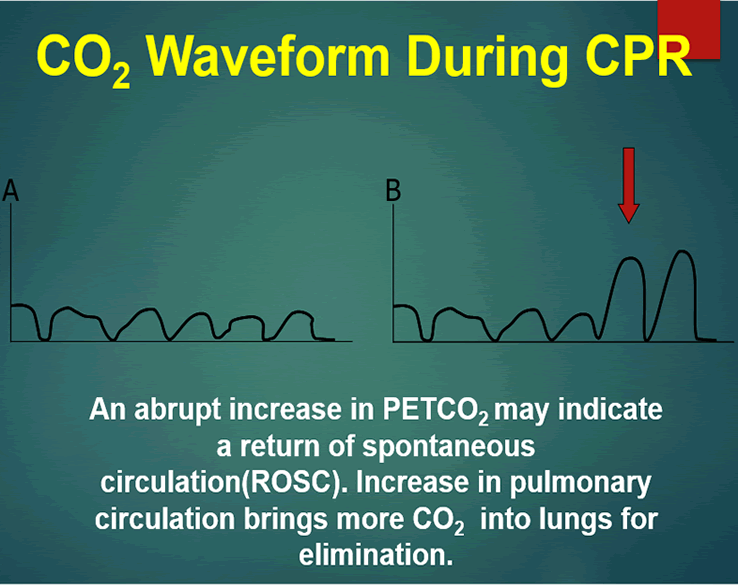
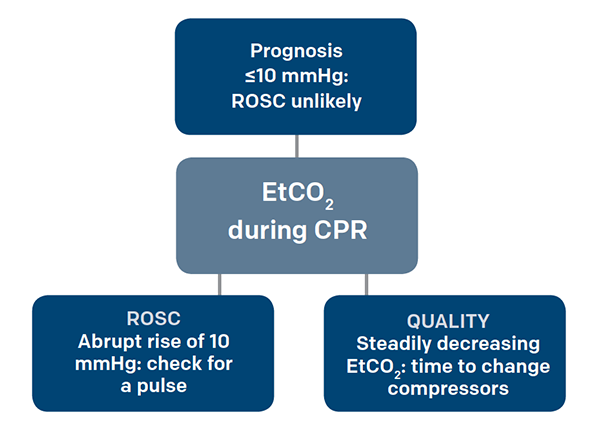
10 to 20 mmHg during CPR was strongly associated with ROSC while persistent EtCO2 below 10 to 20 mmHg after 20 minutes of CPR had a 05 likelihood of ROSC. Continuous Waveform Capnograpy is written as PETCO2 which stands for patient end-tidal carbon dioxide. Rounded low rectangle EtCO 2 waveform during CPR with a high spike on ROSC.
High quality CPR consistent waveform and end-tidal CO2 20 kPa. Numerous studies have shown that abrupt increases in ETCO2 pressures exceeding 10 mmHg that remain higher than preceding values suggest an increase in cardiac output and is indicative of ROSC hence the incorporation of such measures in ACLS guidelines1 Patients with values less than 10 mmHg are more likely to die during CPR and. We compared ETCO2-directed chest compressions with chest compressions optimized to pediatric basic life support guidelines in an infant swine model to.
Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45 mmHg. Another use of ETco 2 monitoring is during procedural sedation and analgesia PSA. Patient end-tidal carbon dioxide.
Evidence suggests a persistently low ETco 2 value and a widened Paco 2-to-ETco 2 gradient during CPR are associated with poor outcomes. Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation CPR ETCO2 concentration is a reliable index of effective heart compression during CPR which is associated with cardiac output 7 8The first sign of the return of spontaneous circulation ROSC during CPR is increase in ETCO2 therefore monitoring of ETCO2 provides very useful information to. 35-40 mm Hg PETCO2 less than 10 indicates ineffective chest compressions.
Low end tidal co2 during cpr. 4 to 5 CO2 PetCO2 vs. Goal is 10 mmHg during CPR.
During CPR ETCO2 levels were initially high decreased to low levels and increased again at ROSC. By measuring exhaled CO2 many types of pulmonary assessments can be made. 20 mmHg at 20 minutes CPR - higher chance of ROSC.
Gradual fall in ETCO2 suggests compressionist fatigue during CPR - time to change compressionists. The normal values are 5 to 6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg. Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement.
End-tidal carbon dioxide. Throughout the resuscitation end-tidal CO 2 was consistently in the 28-36 mmHg range during VFCPR. The height of the etco2 waveform during cpr has been used as an indirect measure of adequate chest compressions helping those involved in resuscitation monitor the effectiveness of their compressions in real time.
Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45 mmHg. End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a noninvasive technique which measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath which is expressed as a percentage of CO2 or mmHg. These levels of CO 2 were consistent with effective chest compression generating reasonable pulmonary blood flow justifying continuation of resuscitation.
Two very practical uses of waveform capnography in CPR are. Abrupt increase in ETCO2 suggests ROSC during CPR detectable before pulse check ETCO2 at 20 minutes of CPR is prognostically useful. A rapid rise in EtCO 2 during CPR can indicate ROSC due to the improved oxygen delivery to tissues that were compromised during cardiac arrest.
Expect it to be as high as 60 mmHg when ROSC is achieved. This pattern not previously described is different from that observed in animal and adult cardiac arrest caused by ventricular fibrillation during which ETCO2 decreases to almost zero after the onset of arrest begins to increase after the onset of effective CPR and increases to. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 correlates with systemic blood flow and resuscitation rate during cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR and may potentially direct chest compression performance.
Ensure proper rate approximately 100min Ensure proper depth with adequate releaserecoil of thorax 12 thorax or minimum 25 inches Persistently low EtCO. 1 evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions and 2 identification of ROSC.

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Capnography During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Current Evidence And Future Directions
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education
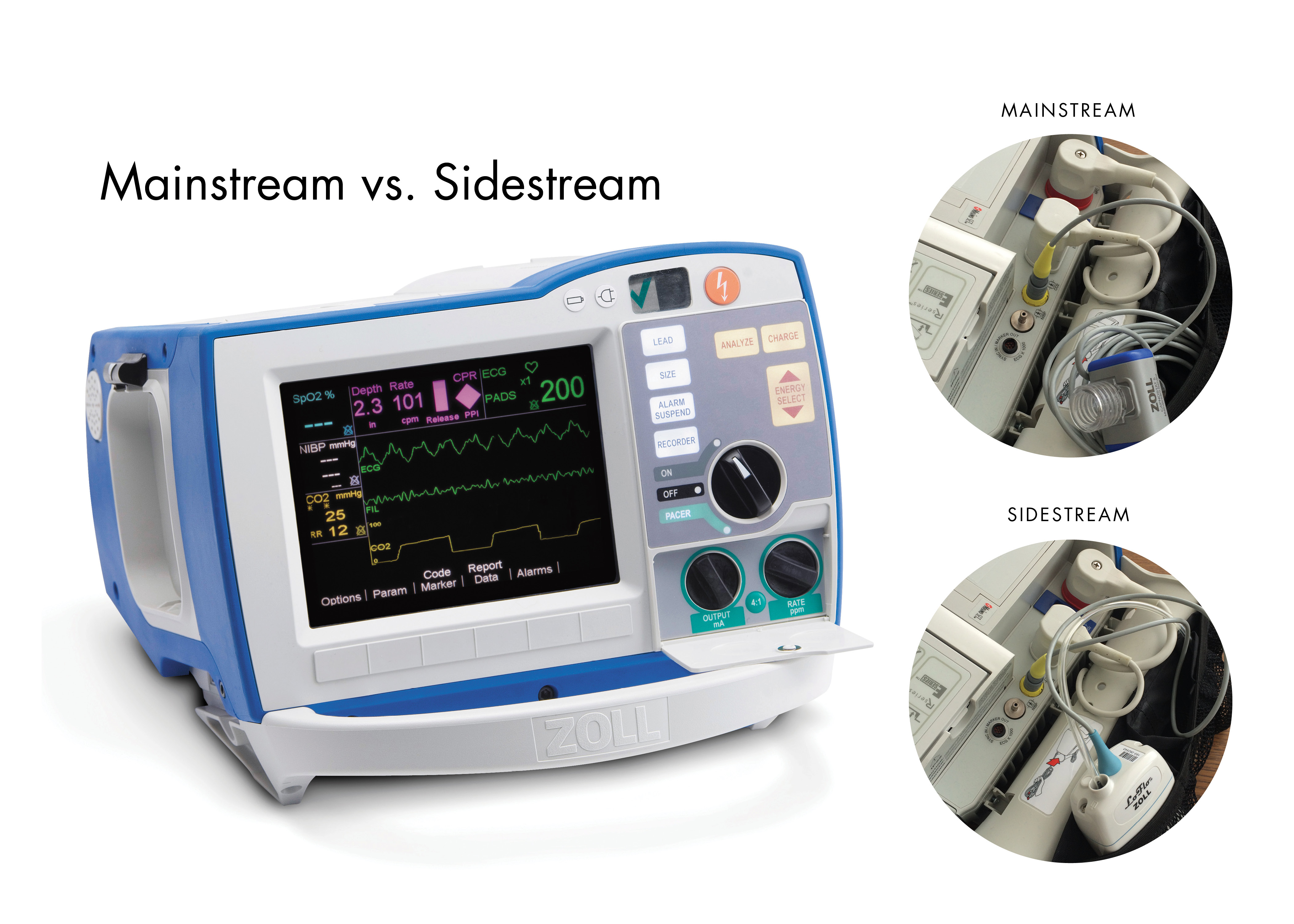
R Series End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Zoll Medical

Capnograph Note Try To Maintain Etco2 Above 10mmhg During Cpr Respiratory Therapy Student Nurse Anesthesia Emergency Nursing
Use End Tidal Capnography For Placing Orogastric Nasogastric Tubes And Cpr Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation
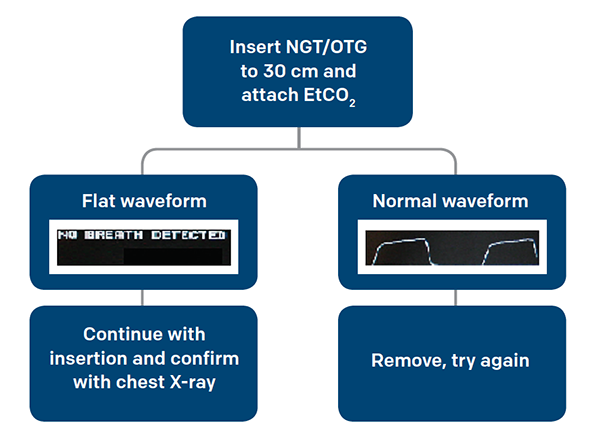
Use End Tidal Capnography For Placing Orogastric Nasogastric Tubes And Cpr Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

The Role Of Etco2 In Termination Of Resuscitation Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News